Hemorrhoids, commonly known as piles, are swollen veins in the lower rectum or anus that can cause discomfort, pain, and bleeding. They are classified into two main types: internal hemorrhoids and external hemorrhoids, each presenting unique symptoms, causes, and treatment options. Understanding the differences between these types is crucial for effective management and relief.
In this blog, we will explore the key differences between internal and external hemorrhoids, their symptoms, causes, and available treatments. By the end, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of how to recognize and address these common yet often misunderstood conditions.
Also Read: Hemorrhoids Symptoms: A Comprehensive Guide to Causes, Types, and Treatments
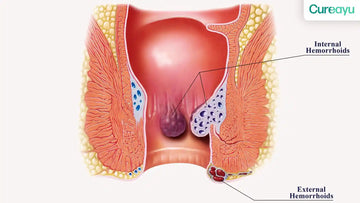
Difference Between Internal and External Hemorrhoids
Location:
- Internal hemorrhoids develop inside the rectum, above the dentate line. They are usually not visible or palpable unless they prolapse.
- External hemorrhoids form under the skin around the anus, below the dentate line, making them visible and often more painful.
Pain Sensation:
- Internal hemorrhoids are usually painless due to the lack of pain-sensitive nerves in the rectum.
- External hemorrhoids can be quite painful because the area around the anus is rich in pain receptors.
Symptoms:
- Internal hemorrhoids often cause bleeding during bowel movements but may not result in discomfort unless prolapsed.
- External hemorrhoids may cause significant pain, swelling, and itching.
Severity:
- Internal hemorrhoids are graded on a scale from I to IV, depending on their degree of prolapse.
- External hemorrhoids do not have such grading but can become thrombosed, leading to acute pain and swelling.
Also Read: Understanding the Difference Between Piles, Fissure, and Fistulas: A Complete Guide
Symptoms of Internal Hemorrhoids
- Rectal Bleeding
Bright red blood is often noticed on toilet paper or in the stool. This is a hallmark symptom of internal hemorrhoids, especially in their early stages.
- Prolapse
As the condition progresses, internal hemorrhoids may prolapse or protrude from the anus during bowel movements. They may retract on their own or require manual adjustment.
- Mucous Discharge
Prolapsed internal hemorrhoids can cause a mucous discharge, which may irritate the surrounding skin and lead to itching.
- Itching and Irritation
Chronic discharge or stool leakage due to prolapsed hemorrhoids can result in persistent itching and skin irritation around the anus.
Symptoms of External Hemorrhoids
- Pain and Discomfort
External hemorrhoids can cause sharp pain, especially during bowel movements or while sitting for extended periods.
- Swelling Around the Anus
A lump or swelling near the anus is a common symptom of external hemorrhoids. This lump can become tender and inflamed.
- Itching and Burning Sensation
The inflamed tissue often leads to intense itching and a burning sensation around the anal region.
- Bleeding
Although less common than internal hemorrhoids, external hemorrhoids can bleed if they become irritated or ruptured.
Also Read: Fistula Symptoms: Understanding Its Causes, Signs, and Treatment Options
Causes of Internal Hemorrhoids
- Chronic Constipation
Straining during bowel movements puts excessive pressure on the rectal veins, leading to internal hemorrhoid formation.
- Sedentary Lifestyle
Prolonged sitting, especially on hard surfaces, increases rectal vein pressure, contributing to the development of internal hemorrhoids.
- Pregnancy
Hormonal changes and increased pressure on the pelvic veins during pregnancy are common causes of internal hemorrhoids.
- Low-Fiber Diet
A diet lacking sufficient fiber leads to hard stools and straining, which can trigger hemorrhoid formation.
Causes of External Hemorrhoids
- Heavy Lifting
Repetitive heavy lifting or strenuous activities can increase abdominal pressure and lead to external hemorrhoids.
- Obesity
Excess body weight puts additional strain on the veins in the pelvic and rectal areas, increasing the risk of external hemorrhoids.
- Prolonged Sitting
Sitting for long periods, especially on the toilet, can cause blood to pool in the veins around the anus.
- Chronic Diarrhea
Frequent bowel movements and irritation of the anal area can lead to external hemorrhoid development.
Also Read: Can Piles Be Cured Without Surgery: A Complete Guide to Natural Treatment
Internal Hemorrhoids Treatment
- Dietary Changes
Increasing fiber intake through fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can soften stools and reduce straining.
- Hydration
Drinking plenty of water helps maintain stool consistency and prevents constipation.
- Medications
Over-the-counter creams, ointments, and suppositories can provide temporary relief from irritation and swelling.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures
Treatments like rubber band ligation, sclerotherapy, or infrared coagulation are effective for internal hemorrhoids that do not respond to conservative measures.
- Surgical Intervention
For severe cases, hemorrhoidectomy or stapled hemorrhoidopexy may be required to remove or reposition the hemorrhoids.
External Hemorrhoids Treatment
- Topical Treatments
Creams and ointments containing hydrocortisone or witch hazel can reduce swelling and discomfort.
- Warm Sitz Baths
Soaking the affected area in warm water several times a day can relieve pain and promote healing.
- Pain Relievers
Oral pain relievers, such as ibuprofen, can help manage severe pain caused by thrombosed external hemorrhoids.
- Thrombectomy
In cases of thrombosed external hemorrhoids, a minor surgical procedure may be needed to remove the clot and relieve pain.
Conclusion
Internal and external hemorrhoids are common conditions that can significantly impact your quality of life if left untreated. Understanding their differences, symptoms, and causes is the first step toward effective management. Internal hemorrhoids often present with painless bleeding and prolapse, while external hemorrhoids are more likely to cause pain, itching, and swelling.
Both types have unique causes, ranging from lifestyle factors to medical conditions like pregnancy and obesity. Fortunately, a range of treatment options—from dietary changes to minimally invasive procedures and surgical interventions—are available to provide relief.
By addressing the underlying causes and adopting healthy habits, you can manage hemorrhoids effectively and prevent their recurrence. If symptoms persist or worsen, consulting a healthcare professional is essential for tailored treatment and long-term relief.